A breath of fresh air fills your lungs revitalizing every cell in your body. Breathing treatments are a lifeline for many individuals grappling with respiratory challenges. It plays a crucial role in restoring the rhythm of effortless breathing. But here’s the catch – have you ever wondered how long breathing treatments last?
Understanding the duration of breathing treatments is not just a matter of curiosity. It’s a key piece of the puzzle that holds the power to transform the way we manage respiratory health. In the next few paragraphs, we’ll explore the intricacies of breathing treatments. You can unravel the enigma of their duration and why it matters more than we might think. So, let’s take a deep breath and embark on this journey of knowledge together.
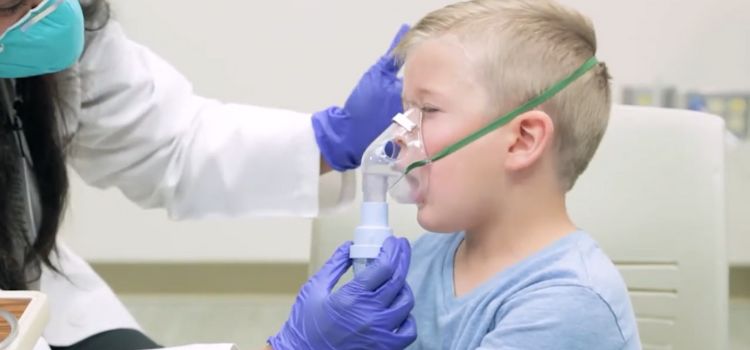
Different Types of Breathing Treatments
When it comes to respiratory care. A diverse array of breathing treatments stands ready to offer you relief and support. Among the most prevalent methods are inhalers and nebulizers. Each wielding its own set of advantages in the battle for better breathing.
1. Inhalers as Your Breathing Treatment
Inhalers, those pocket-sized powerhouses, are like the superheroes of respiratory care. With a quick press, they deliver a measured dose of medication straight to the lungs. Portable and discreet, inhalers are the go-to choice for those needing a rapid response to manage conditions like asthma. Think of them as the caped crusaders, swooping in precisely when needed.
2. Nebulizers as Your Breathing Treatment
On the other hand, nebulizers take a different approach. Nebulizers transform liquid medication into a fine mist that’s inhaled through a mask or mouthpiece. This method is often favored for children and elderly, or those who struggle with the coordination required for inhalers. Nebulizers are like steady and reliable companions. It ensures a slow and steady release of medication for a more extended therapeutic effect.
3. Positive Expiratory Pressure (PEP) Therapy
Then there’s the less common, yet equally important, positive expiratory pressure (PEP) therapy. It involves exhaling against resistance. Which helps keep the airways open. It’s like the workout regimen for your respiratory system. Strengthening your lungs and making each breath more efficient.

This mechanism has the potential to enhance mucus clearance. That promotes the accumulation of gas behind the mucus through collateral ventilation. It’s temporarily boosting your functional residual capacity with a more effective respiratory process.
How Do Nebulizer Treatments Work?
Have you ever wondered about the magic behind the mist when it comes to nebulizer treatments? Let’s uncover the secrets of this respiratory wizardry.

Nebulizers operate on a simple yet ingenious principle. At the heart of the mechanism is the nebulizer cup. Which is a small container where liquid medication is transformed into a fine mist. You may picture it as a tiny cauldron that brewing a concoction of relief for your lungs. The nebulizer’s compressor generates a steady flow of air and creates a low-pressure zone. This prompts the liquid medication to be drawn up from the cup and broken into minuscule droplets.
Importance of Nebulizer Cup in Creating a Fine Mist
Now, the importance of the nebulizer cup cannot be overstated. It’s the maestro orchestrating the symphony of mist. That ensures the medication is finely atomized for optimal inhalation. Think of it as the conductor guiding each note to create a harmonious melody of respiratory relief. The result? A cloud of microscopic medication particles ready to dance their way deep into your airways. Providing you with targeted and efficient treatment.
Factors That Affecting the Duration of Breathing Treatments
The duration of your breathing treatments is like a dynamic equation. Which is influenced by a myriad of factors that uniquely shape each individual’s respiratory journey.
– Impact of the specific breathing problem
First and foremost, the nature and severity of the specific breathing problem are paramount. Conditions vary widely, from mild asthma to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Each of them demands a tailored approach. The complexity of the ailment directly impacts how long the therapeutic effects of a breathing treatment linger.
– Individual responsiveness to treatments
Equally pivotal is an individual’s responsiveness to treatments. Our bodies are not one-size-fits-all and the same holds true for respiratory systems. Some individuals experience rapid relief. While others may require a more extended duration to witness the full benefits. It’s akin to different musical instruments responding uniquely to the same melody, each requiring its tempo and rhythm.
– Frequency and consistency of treatments
The frequency and consistency of your treatments also play a starring role in the duration equation. Think of it as a fitness regimen for your lungs. The more regular and committed the practice, the better the outcomes. Skipping sessions or inconsistent treatment can disrupt the flow of respiratory well-being, akin to missing beats in a song.
How Long Do Breathing Treatments Last?
Depending on various treatment methods normally the breathing treatment lasts between 5-20 minutes. The diverse methods available provide unique durations customized to suit individual needs. Here are the specific durations for each type of treatment method,
Inhalers: The swift superheroes of respiratory care. Inhalers typically require a mere 5-10 minutes to administer a dose. It gives quick and efficient and the sprinters of the treatment track. Inhalers can swiftly tackle respiratory challenges.
Nebulizer treatments: On the other hand, unfold at a more leisurely pace. The magic in the mist takes around 10-20 minutes to weave its therapeutic charm. Here, the 20-minute mark emerges as a significant milestone. That signifies the optimal time for the nebulizer cup to concoct a mist of microscopic medication particles. It’s like a short intermission in the respiratory drama. Which allows you to inhale deeply and embrace the full spectrum of relief.
Positive Expiratory Pressure (PEP) Therapy:
PEP therapy sessions typically range from 15 to 30 minutes. It offers a moderate yet effective commitment in the quest for enhanced lung health. The duration provides you sufficient time for the respiratory muscles to engage. Which promotes the clearance of your mucus and maintains airway openness.
The Role of Face Masks in Various Breathing Treatments
Face masks are often the unsung heroes of your breathing treatments. This face mask plays a pivotal role in ensuring the effectiveness and comfort of various respiratory therapies.
For the nebulizer treatments, face masks act as the bridge connecting the mist to the lungs. They create a sealed environment. Allowing you to inhale the fine mist with precision. The fit of the mask is like a tailored suit. That ensures the therapeutic mist reaches its destination without unnecessary leaks or interruptions. This intimate connection enhances the efficiency of the treatment, making every breath count.
In the case of Positive Expiratory Pressure (PEP) Therapy, face masks come into play to maintain a controlled exhale against resistance. They serve you as the gateway for the expelled air. Which creates the necessary pressure to keep the airways open.
Impact of the Face Mask in Treatment Duration
However, it’s important to note that while face masks are instrumental. However, their impact on your breathing treatment duration is minimal. Whether with an inhaler, nebulizer, or PEP therapy, additional time is spent to secure a proper fit. That is a negligible investment in your overall respiratory well-being. The right mask ensures that each breath during the treatment is not only effective but also a comfortable pleasant experience.
Effect of Air Compressors in the Context of Breathing Treatments
The air compressor functions as the engine of the nebulizer. It generates a continuous flow of compressed air. That propels the medication from the nebulizer cup to your airways. It’s the unseen force breathing life into every misty particle. Which ensures that the respiratory magic unfolds seamlessly.
How Air Compressors Influence Breathing Treatment Duration?
The air compressor sets the tempo for the nebulizer dance. The power and efficiency of the compressor determine how quickly the mist is created. Which directly impacts the time it takes for individuals to inhale the prescribed dosage. Like the conductor guiding a musical performance. The air compressor ensures that the respiratory melody is both precise and harmonious. So the air compressors contribute to an optimal and timely delivery of respiratory relief. Which improves the duration of beating treatment.
Side Effects of Prolonging The Breathing Treatments
Breathing treatments are a lifeline for managing your respiratory conditions. It’s crucial to be aware that prolonged or improper use can introduce a set of potential side effects for you. You can underscore the importance of adhering to recommended treatment durations.
- One common side effect is the development of oral thrush. A fungal infection in your mouth. This can be attributed to the steroids often present in inhalers. The moist environment created by the medication residue provides an ideal breeding ground for the fungus. Which leads your mouth to feel discomfort and an unpleasant taste. You can mitigate this risk by regular mouth rinsing after the use inhaler.
- Another concern arises from the prolonged use of nebulizer treatments. Particularly if you are not properly cleaned. The mist created by the nebulizer carries the risk of delivering bacterial or fungal particles into your respiratory system. Which potentially causes infections in your respiratory system. You can mitigate this risk by regular cleaning and maintenance of the nebulizer equipment.
- In the case of Positive Expiratory Pressure (PEP) Therapy, excessive use may lead to respiratory muscle fatigue. While the therapy aims to strengthen the respiratory muscles. The overexertion without adequate rest intervals can have the opposite effect. Which causes fatigue and discomfort.
- Beyond physical side effects, there’s the psychological impact of extended treatments. The monotony of daily sessions, especially for chronic conditions, may contribute to treatment fatigue and reduced adherence. This can result in a decreased willingness to continue the prescribed therapy. That’s potentially undermining its long-term effectiveness.
The Cost of Breathing Treatments
The cost of breathing treatments can vary widely based on several factors. Including the specific type of treatment, the frequency of use, and whether generic or brand-name medications are prescribed. Here’s a general overview:
Inhalers:
- Generic inhalers tend to be more cost-effective, ranging from $20 to $50 per inhaler.
- Brand-name inhalers can be significantly more expensive, ranging from $50 to over $200 per inhaler.
Nebulizer Treatments:
- Nebulizer costs vary, with compressor nebulizers generally ranging from $50 to $200.
- Disposable nebulizer kits, which include medication vials and masks, can cost around $5 to $20 each.
Positive Expiratory Pressure (PEP) Devices:
- PEP therapy devices typically range from $30 to $100, depending on the brand and features.
Tips on Managing and Reducing Costs
– First, exploring generic alternatives to brand-name medications can significantly cut expenses without compromising efficacy. Generic versions often contain the same active ingredients, providing a more budget-friendly option.
– Investigating patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies is another avenue. These programs may provide you with financial assistance or discounts for prescribed medications.
– Furthermore, discussing treatment costs with healthcare providers can lead to tailored solutions. Providers may offer insights into cost-effective alternatives or recommend assistance programs that align with your financial situation.
Tips for Maximizing the Effectiveness of Breathing Treatments
To optimize the effectiveness of breathing treatments, proper use of inhalers and nebulizers is paramount. Here are some essential tips:
1. Mastering Inhaler Techniques:
- You have to the correct inhaler technique to ensure the medication reaches your lungs efficiently. Follow the prescribed steps, such as coordinating inhalation with actuation. Then consider using a spacer device for improved drug delivery.
2. Nebulizer Best Practices:
- For nebulizer users, adhere to the recommended dosage and duration of the treatment. Keep your device clean, as any residue may hinder its efficiency.
3. Consistent Medication Schedule:
- You have to establish a consistent schedule for taking your medications. Regularity in treatment helps maintain optimal lung function and provides better control over your respiratory symptoms. Set reminders if necessary to ensure adherence to your prescribed regimen.
Monitor Your Symptoms:
- Stay vigilant about changes in your symptoms. If you notice any deterioration or unexpected side effects. Consult your healthcare provider promptly for adjustments to your treatment plan.
Incorporating healthy habits for better respiratory health
In addition to using inhalers and nebulizers effectively, incorporating healthy habits can enhance respiratory health:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen respiratory muscles and improve lung capacity. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can contribute to overall respiratory fitness.
- Hydration is Key: Maintain proper hydration levels to keep the airways moist and facilitate mucus clearance. Sufficient water intake supports respiratory health and reduces the risk of infections.
- Avoiding Respiratory Irritants: Minimize exposure to smoke, pollutants, and allergens. Quit smoking if applicable, and ensure your living environment is smoke-free.
- Balanced Nutrition: You have to consume a well-balanced diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins. Which play a crucial role in supporting respiratory health. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins contribute to overall well-being.
Benefits of Consistent Breathing Treatments
Consistent breathing treatments offer a wealth of benefits. It acts as a cornerstone for improved respiratory health. By diligently adhering to prescribed treatments, you may experience enhanced management of breathing problems. Which gives you a more stable and controlled respiratory state.
Importantly, this consistency acts as a formidable shield against exacerbations and complications. Regular treatments contribute to your proactive symptom control. Reducing the likelihood of your respiratory flare-ups and potential complications. In essence, the simple act of staying consistent with breathing treatments becomes a powerful strategy for you in your optimal lung health.
🔗Related Article: What is The Purpose of Breathing Exercises?
Conclusion
In the mystery of “How Long Do Breathing Treatments Last, understanding the diverse landscape of breathing treatments is essential. From inhalers and nebulizers to Positive Expiratory Pressure (PEP) therapy, each method plays a unique role in the orchestration of optimal lung health.
The duration of breathing treatments is influenced by individual factors and treatment type is a crucial element in this harmony. By embracing the benefits of consistent treatments, you not only manage breathing problems effectively but also prevent complications. Let’s breathe easy by staying attuned to personalized plans.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Regular cleaning is recommended after each use to maintain hygiene and ensure optimal functionality.
Nebulizers are suitable for both chronic and acute respiratory issues. However, specific guidance from a healthcare professional is essential.
Face masks are commonly used, but alternatives like mouthpieces may be available based on your preferences and comfort.
No, the duration varies among inhalers. Some may require a few minutes, while others may take longer.
Exploring insurance coverage, assistance programs, and generic medication options can help in managing and reducing the cost of breathing treatments.
Leave a Reply